Using ROS for Linux
Robot Operating System (ROS) provides libraries and tools to help software developers create robot applications. It provides hardware abstraction, device drivers, libraries, visualizers, message-passing, package management, and more. This document shows how to install arena_camera, LUCID’s ROS driver.
System Requirements
- Ubuntu 16.04 or Ubuntu 18.04
- ROS Kinetic for Ubuntu 16.04 or ROS Melodic for Ubuntu 18.04
- Arena SDK for Linux x64 v0.1.26 or higher
- Driver file: arena_camera_ros found at https://github.com/lucidvisionlabs/arena_camera_ros/releases/
Initial ROS Setup
-
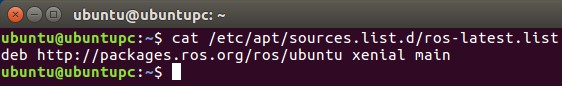
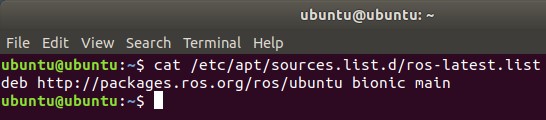
Set up your system to acquire software from packages.ros.org.
$ sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://packages.ros.org/ros/ubuntu $(lsb_release -sc) \main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ros-latest.list'You can confirm the new list file is set by checking the contents of ros-latest.list:
-
Use apt-key to install the Open Robotics key to your list of trusted keys.
$ sudo apt-key adv --keyserver 'hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80' --recv-key C1CF6E31E6BADE8868B172B4F42ED6FBAB17C654 -
Install ROS Desktop. The following commands will install ROS onto the system.
On Ubuntu 16.04 (xenial):
$ sudo apt-get update$ sudo apt-get install ros-kinetic-desktop-fullOn Ubuntu 18.04 (bionic):
$ sudo apt-get update$ sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-desktop-full -
Initialize rosdep. This will setup system dependencies for ROS.
$ sudo apt-get install python-rosdep$ sudo rosdep init$ rosdep update -
Setup ROS environment variables.
On Ubuntu 16.04 (xenial):
$ echo "source /opt/ros/kinetic/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc$ source ~/.bashrcOn Ubuntu 18.04 (bionic):
$ echo "source /opt/ros/melodic/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc$ source ~/.bashrc -
Install ROS package workspace dependencies. This will allow you to create and manage your own ROS workspaces, including the ROS workspace used by arena_camera.
$ sudo apt-get install python-rosinstall python-rosinstall-generator python-wstool build-essential
Arena SDK Setup
-
Download and install Arena SDK. Arena SDK for Linux is available on the Downloads page at https://dev.thinklucid.com/downloads-hub/. The Arena SDK dependencies are listed in the README file included with the SDK.
Creating a ROS workspace for the arena_camera ROS Driver
-
Set up your system to acquire software from packages.ros.org.
-
Set up your ARENA_CONFIG_ROOT environment variable. This is also the path to the ROS workspace used by arena_camera.
$ echo "export ARENA_CONFIG_ROOT=~/catkin_ws" >> ~/.bashrc$ source ~/.bashrc
Building and Running the arena_camera ROS Driver
-
-
Navigate to your arena_camera ROS workspace
-
$ cd ~/catkin_ws-
Copy the included image_encoding.h to your ROS include folder
On Ubuntu 16.04 (xenial):
$ sudo cp /opt/ros/kinetic/include/sensor_msgs/image_encodings.h /opt/ros/kinetic/include/sensor_msgs/image_encodings.h.bak$ sudo cp inc/image_encodings.h /opt/ros/kinetic/include/sensor_msgs/image_encodings.hOn Ubuntu 18.04 (bionic):
$ sudo cp /opt/ros/melodic/include/sensor_msgs/image_encodings.h /opt/ros/melodic/include/sensor_msgs/image_encodings.h.bak$ sudo cp inc/image_encodings.h /opt/ros/melodic/include/sensor_msgs/image_encodings.h
-
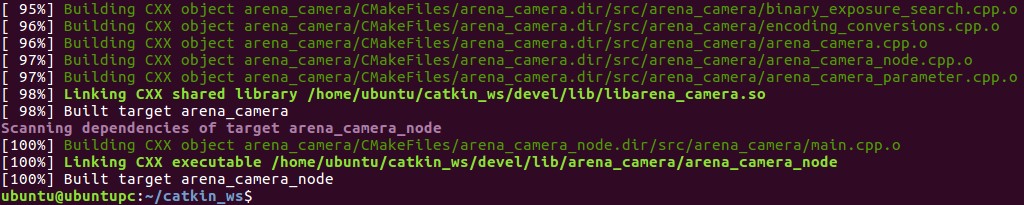
Build arena_camera
$ catkin_makeThe above command will build:
• arena_camera: The Arena SDK camera code for ROS. • arena_camera_node: The ROS node for arena_camera. See
http://wiki.ros.org/ROS/Tutorials/UnderstandingNodes
for further information. -
Run roscore to start the ROS server
$ roscore
-
Run arena_camera as a node in a new terminal. The first command listed below will overlay your workspace on top of your ROS environment. The second command will connect to the camera and the camera will start imaging. The received images will be published to a topic. See http://wiki.ros.org/Topics and http://wiki.ros.org/ROS/Tutorials/UnderstandingTopics for further information.
$ source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash$ rosrun arena_camera arena_camera_node -
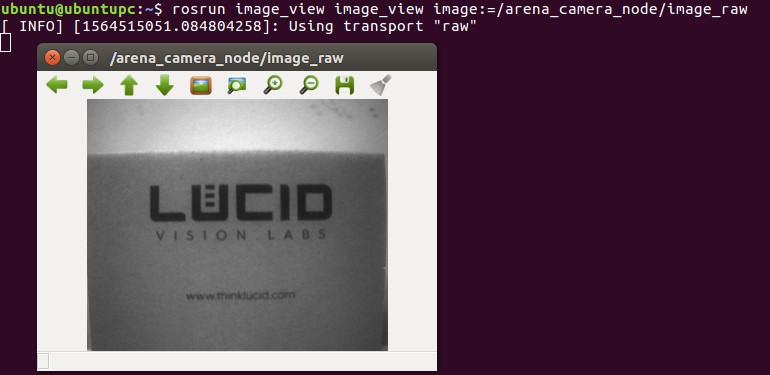
View the raw images by opening a new terminal and subscribing the image_view node to topic name image_raw.
$ rosrun image_view image_view image:=/arena_camera_node/image_raw
Using rosparam to Set Camera Parameters
-
ROS includes the rosparam tool which can be used to set camera parameters before starting arena_camera.
To set a parameter:
$ rosparam set /arena_camera_node/<parameter_name> value$ rosparam set /arena_camera_node/frame_rate 10$ rosparam set /arena_camera_node/image_encoding mono8To list of parameters that are already set:
$ rosparam list /arena_camera_nodeTo view a set parameter’s value:
$ rosparam get /arena_camera_node/<parameter_name>$ rosparam get /arena_camera_node/frame_rateTo delete a set parameter:
$ rosparam delete /arena_camera_node/<parameter_name>$ rosparam delete /arena_camera_node/frame_rate
Other rosparam commands
| Command | Description |
| rosparam dump | Dump current parameters to a file |
| rosparam load | Load parameters from a file |
Supported arena_camera_node Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
| device_user_id | Device User ID (user defined name) |
| frame_rate | Frame Rate (Hz) |
| image_encoding | Pixel Format |
| binning_x | Binning parameter for X axis (must match binning_y) |
| binning_y | Binning parameter for Y axis (must match binning_x) |
| exposure | Exposure Time (microseconds) |
| gain | Gain (dB) |
| gamma | Gamma correction of pixel intensity/td> |
| exposure_auto | Auto Exposure control (true/false) |
| gain_auto | Auto Gain control (true/false) |
ROS camera_calibration Node
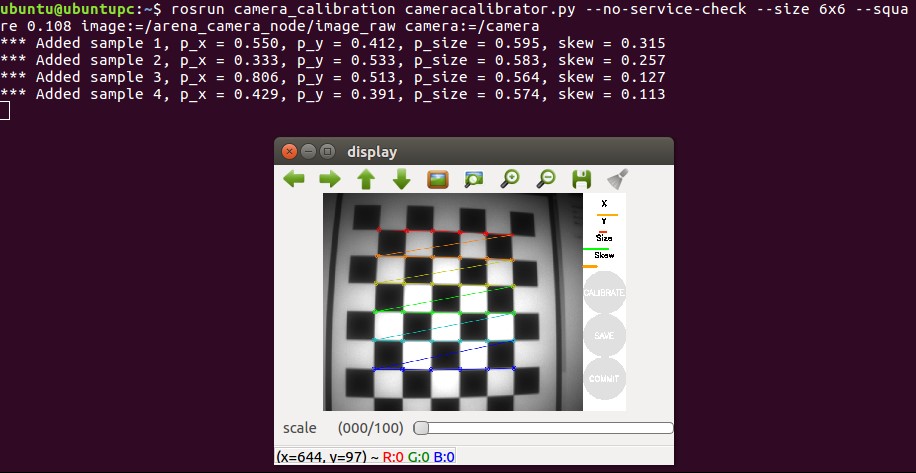
An optional step is to calibrate a single camera using the ROS camera_calibration node. This will assist in calibrating a monocular camera from the image_raw topic. See http://wiki.ros.org/camera_calibration/Tutorials/MonocularCalibration for more detailed information.
Once you have installed camera_calibration with rosdep, you can use it with arena_camera:
$ rosrun camera_calibration cameracalibrator.py --no-service-check --size 8x6 --square 0.108 image:=/arena_camera_node/image_raw camera:=/camerawhere 8×6 is the number of vertices in your checkerboard pattern.
Once there is enough data for calibration, click Calibrate to start the calibration process and click Save to save the calibration data to a file.
Once the calibration data is saved to file, you can extract the calibration tarball contents and apply the calibration to the camera using rosparam. The following steps assume the calibration data is extracted to ~/calibration.
$ mkdir ~/calibration$ tar -xvf /tmp/calibrationdata.tar.gz -C ~/calibration$ rosparam set /arena_camera_node/camera_info_url "file://home/ubuntu/calibration/ost.yaml"$ rosrun arena_camera arena_camera_node